11438번: LCA 2
첫째 줄에 노드의 개수 N이 주어지고, 다음 N-1개 줄에는 트리 상에서 연결된 두 정점이 주어진다. 그 다음 줄에는 가장 가까운 공통 조상을 알고싶은 쌍의 개수 M이 주어지고, 다음 M개 줄에는 정
www.acmicpc.net
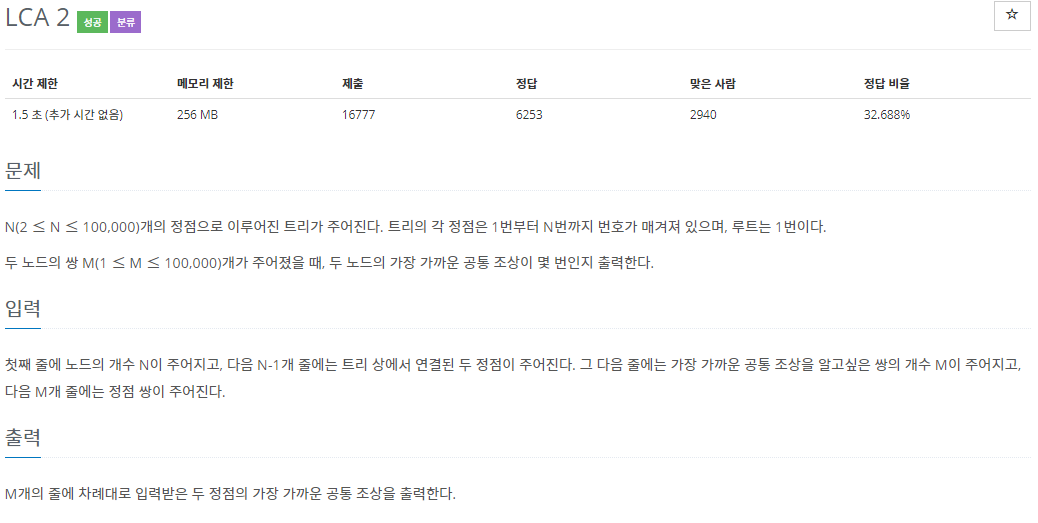
1. dfs를 통해서 자신의 부모만 구함.
2. 이중 for문을 통해서 조상을 셋팅함
- tmp = ancestor[j][i-1]은 j의 2^i-1만큼 위에 있는 조상
- ancestor[j][i] 는 ancestor[tmp][i-1]; 나의 8(2^3)번째 조상은 나의 4(2^2)번째 조상의 4(2^2)번째 조상이다.
3. 두 노드의 가장 까까운 조상 출력
- 필요할 경우 swap
- 더 깊이 있는 노드를 끌어올려서 높이를 맞춤
- 같은 높이일때 두 노드의 값이 같으면 종료
- 같은 높이일때 두 노드의 값이 다르면 두 노드의 높이를 올려가면서 체크
자세한건 주석을 보시면 좀더 이해가 되실겁니다 .ㅎ

import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// LCA 2 문제 - 11438번
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int n,m;
static int[][] ancestor;
static int[] depth;
static boolean[] visited;
static int maxHeight = 18; // n의 최대값까지 포함하는 높이를 미리 설정 - 2^18 = 131,072, n의 최대값 100,000
static List<Integer>[] graph;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
graph = new ArrayList[n+1];
visited = new boolean[n+1];
depth = new int[n+1];
ancestor = new int[n+1][maxHeight];
for (int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph[a].add(b);
graph[b].add(a);
}
// 루트 1의 부모를 1로 설정하도록 매개변수 설정
dfs(1,1,1);
for (int i=1; i<maxHeight; i++){
for (int j=1; j<=n; j++){
int tmp = ancestor[j][i-1];
ancestor[j][i] = ancestor[tmp][i-1]; // 나의 8(2^3)번째 조상은 나의 4(2^2)번째 조상의 4(2^2)번째 조상이다.
}
}
m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i=0; i<m; i++){
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
sb.append(LCA(a, b)).append('\n');
}
System.out.print(sb);
}
static void dfs(int parent, int cur, int dep){
if (visited[cur]) return;
visited[cur] = true;
depth[cur] = dep;
ancestor[cur][0] = parent;
for (int i=0; i<graph[cur].size(); i++){
dfs(cur, graph[cur].get(i), dep+1);
}
}
static int LCA(int a, int b){
// a가 더 덜 깊은 경우 a와 b를 swap
// swap을 하지않으면 아래 로직을 if문으로 분기 해야하기 때문에
if(depth[a] < depth[b]) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// 높이 맞추기
// 높이의 차이 만큼 a의 높이를 올림
// 차이가 만약 5 라면 101
// 100(i = 2) a을 4만큼 끌어 올리고
// 그럼 차이는 1되고
// 1(i = 0) 일때 a을 1만큼 끌어올려서 높이를 마추게 된다.
for (int i = maxHeight - 1; i>=0; i--) {
if (depth[a] - depth[b] >= (1 << i)) {
a = ancestor[a][i];
}
}
// 높이가 같을때 같은 경우
if (a == b) return a;
// 높이를 같이 올라가면서 같은 경우
// 루트에 가장 가까운 a != b를 찾아서 변경함
// 2^이 기록되어있기때문에 2^8에서는 같지만 2^4에서는 다를 수 있음
// 만약 9 높이에서 같다면 16에서는 같지만 8에서는 다르기 때문에
// 8(2^3)까지 이동한 뒤 1(2^0)을 더 움직여서 도달한다.
for (int i = maxHeight - 1; i>=0; i--) {
if (ancestor[a][i] != ancestor[b][i]) {
a = ancestor[a][i];
b = ancestor[b][i];
}
}
return ancestor[a][0];
}
}'코딩 테스트 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2618 자바 - 경찰차 문제 (0) | 2021.03.11 |
|---|---|
| 백준 6549 자바 - 히스토그램에서 가장 큰 직사각형 문제 (0) | 2021.03.08 |
| 백준 2169 자바 - 로봇 조종하기 문제 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| 백준 10775 자바 - 공항 문제 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| 백준 11505 자바 - 구간 곱 구하기 (0) | 2021.03.07 |