팩토리 메소드 패턴 :
객체를 생성하기 위한 인터페이스를 정의하는데, 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를만들지는 서브클래스에서 결정하게 만든다. 즉 팩토리 메소드 패턴을 이용하면 클래스의 인스턴스를 만드는 일을 서브클래스에게 맡기는 것.
이점
클래스의 변경사항이 생겼을 때 얼마나 다른 클래스에게도 영향을 줄 것인가가 결합도이다. 팩토리 메소드 패턴은 직접 사용하는 객체를 생성하지 않고 팩토리 메소드 클래스를 통해 객체를 대신 생성하고 그 객체를 반환 받아 사용하기 때문에 효율적인 코드 제어를 할 수 있을 뿐더러 결합도를 낮춰 유지보수가 용이하다.

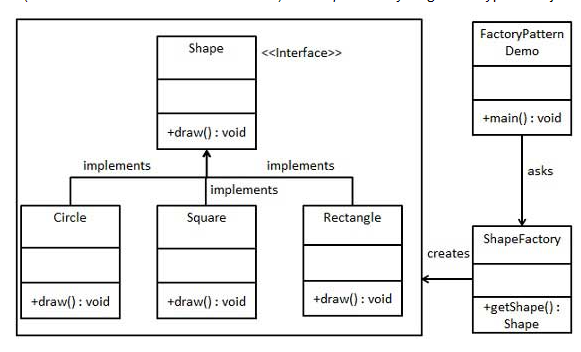
위 설계를 보면
1. Shape라는 인터페이스
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
2. 인터페이스를 상속받은 원, 정사각형, 직사각형 구현
public class Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("원을 그렸습니다.");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("정사각형을 그렸습니다.");
}
}public class Rectangle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("직사각형을 그렸습니다.");
}
}
3. ShapeFactory에서 Shape를 만들어서 리턴하는 메서드 구현
public class ShapeFactory {
public Shape getShape(String shapeType) {
if (shapeType == null) {
return null;
}
switch (shapeType) {
case "CIRCLE" :
return new Circle();
case "SQUARE" :
return new Square();
case "RECTANGLE" :
return new Rectangle();
default:
return null;
}
}
}
4. main()에서 factory를 통해서 shape를 만들기
public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory();
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
print(shape1);
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
print(shape2);
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
print(shape3);
Shape shape4 = shapeFactory.getShape(null);
print(shape4);
Shape shape5 = shapeFactory.getShape("abc");
print(shape5);
}
public static void print(Shape shape) {
if (shape != null) {
shape.draw();
}else {
System.out.println("올바르지않은 모형");
}
}
}5. 결과
원을 그렸습니다.
정사각형을 그렸습니다.
직사각형을 그렸습니다.
올바르지않은 모형
올바르지않은 모형Reference
'Design Pattern > 생성 패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| prototype pattern (0) | 2021.04.13 |
|---|---|
| Builder Pattern (0) | 2021.04.13 |
| Singleton Pattern (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| Abstract Factory Pattern (0) | 2021.04.12 |