prototype pattern
원형이 되는 인스턴스를 사용하여 생성할 객체의 종류를 명시하고, 이렇게 만든 견본을 복사해서 새로운 객체를 생성합니다.
object 생성이 높은 비용으로 수 많은 요청을 하는 경우, 또는 비슷한 object를 지속적으로 생성해야 할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있다. prototype pattern은 본래의 object로 부터 새로운 object를 만들어내며(서로 다른 인스턴스), 각 객체에 따라 데이터 수정이 가능한 메커니즘을 제공
java의 clone()을 이용하기 때문에 생성하고자 하는 객체에 clone에 대한 Override를 요구합니다.
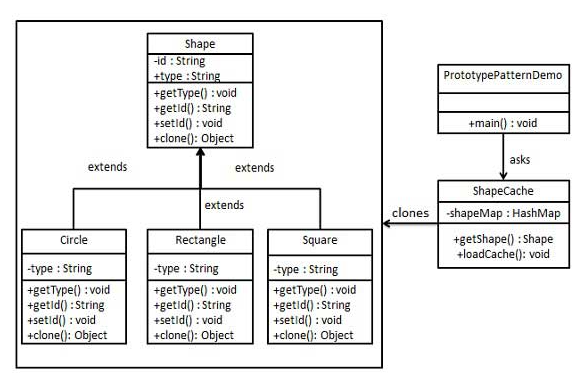
1. Shape 인터페이스 구현
- Cloneable을 상속받아서 clone을 오버라이딩 try catch을 통해서 익셉션을 바로 처리하도록 함
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getType(){
return type;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}
2. Shape를 상속받은 모형 구현
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(){
type = "원";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("원을 그렸습니다.");
}
}public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(){
type = "직사각형";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("직사각형을 그렸습니다.");
}
}public class Square extends Shape {
public Square(){
type = "정사각형";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("정사각형을 그렸습니다.");
}
}
3.shapeCache를 구현
- 데이터를 쌓는 메서드와 cache에서 shape를 넘겨줄때 clone하여 리턴
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeCache {
private static final HashMap<String, Shape> shapeMap = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getShape(String shapeId) {
Shape cachedShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId);
// 클론한 값을 리턴
return (Shape) cachedShape.clone();
}
// Hashtable 데이터 load
public static void loadCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeMap.put(circle.getId(),circle);
Square square = new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeMap.put(square.getId(),square);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle);
}
}4. main()
- cache에 데이터를 load한 뒤 getShape를 통해서 clone한 Shape 가져옴.
public class PrototypePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeCache.loadCache();
Shape clonedShape = ShapeCache.getCloneShape("1");
Shape noClonedShape = ShapeCache.getNoCloneShape("1");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape.getType());
System.out.println("Shape : " + noClonedShape.getType());
System.out.println(clonedShape.equals(noClonedShape));
System.out.println(clonedShape.hashCode());
System.out.println(noClonedShape.hashCode());
System.out.println();
Shape clonedShape2 = ShapeCache.getCloneShape("2");
Shape noClonedShape2 = ShapeCache.getNoCloneShape("2");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape2.getType());
System.out.println("Shape : " + noClonedShape2.getType());
System.out.println(clonedShape2.equals(noClonedShape2));
System.out.println(clonedShape2.hashCode());
System.out.println(noClonedShape2.hashCode());
System.out.println();
Shape clonedShape3 = ShapeCache.getCloneShape("3");
Shape noClonedShape3 = ShapeCache.getNoCloneShape("3");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape3.getType());
System.out.println("Shape : " + noClonedShape3.getType());
System.out.println(clonedShape3.equals(noClonedShape3));
System.out.println(clonedShape3.hashCode());
System.out.println(noClonedShape3.hashCode());
}
}
5. 결과
- clone을 하면 동일하게 type값이 나오지만 equls나 hashcode를 사용하면 동일하지 않다고 나온는 것을 확인 할 수 있다. 즉 clone을 통해서 만든 값은 기존 값과 내용은 같으나 주소값이 다른 다른 객체이다. 이를 통해서 기존 값을 수정하면 안되지만 수정해야하는 로직을 처리해야할때 clone을 통해서 만들고 해당 값을 수정하도록 할 수 있다.
Shape : 원
Shape : 원
false
460141958
1163157884
Shape : 정사각형
Shape : 정사각형
false
1956725890
356573597
Shape : 직사각형
Shape : 직사각형
false
1735600054
21685669'Design Pattern > 생성 패턴' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Builder Pattern (0) | 2021.04.13 |
|---|---|
| Singleton Pattern (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| Abstract Factory Pattern (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| Factory Pattern (0) | 2021.04.12 |